Dholera, India’s first Greenfield Smart City, is being developed with world-class infrastructure, including an advanced water treatment plant and supply system. Given the region’s water scarcity, the Dholera Special Investment Region (DSIR) has planned sustainable water management solutions to ensure a reliable supply for residents, industries, and agriculture.
Water Treatment Plants in Dholera
Two major water treatment plants (WTPs) will be built:
- Near Ottariya Village (For Phase 1 & 2)
- Near Hebatpur Village (For Phase 2 & 3)
- kadipur ( Located strategically near residential zones in DSIR )
These plants will operate in modular stages, expanding as the city grows. They will include:
- Advanced filtration & purification systems
- Storage tanks (1.5 days’ capacity)
- 24 sector-level water distribution points
Water Supply Sources for Dholera
To meet the city’s water demands, multiple sources were evaluated, including:
- Narmada Canal (Primary source)
- Pariyej & Kaneval Reservoirs (Limited availability)
- Local Reservoirs (To be developed)
- Desalination (Future option)
- Groundwater (Not preferred due to poor quality)
- Kalpasar Sweet Water Lake (Future possibility)
After careful study, the Narmada Canal was chosen as the main water source due to its reliability. Additional reservoirs will be built to store water, but since local rivers dry up for 9 months a year, they will be connected to the Narmada Canal for continuous supply.
Why Not Other Sources?
- Pariyej & Kaneval Reservoirs: Already allocated to other users.
- Desalination: Expensive and Dholera is far from the open sea.
- Groundwater: High cost and poor quality make it unsuitable.
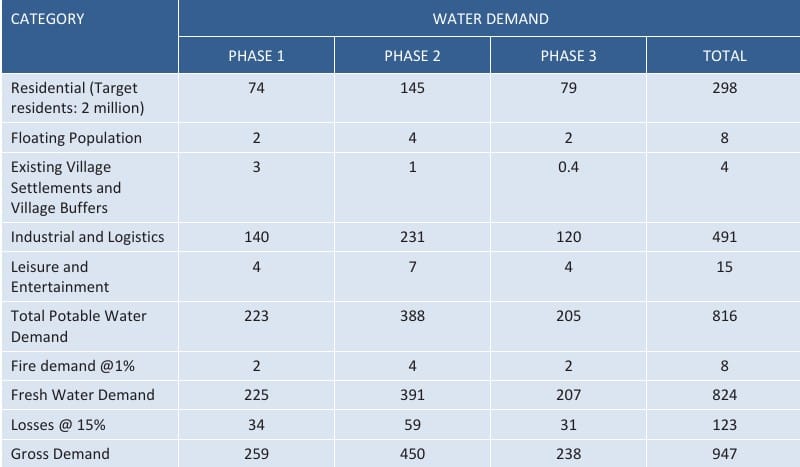
Water Demand & Recycling
Dholera’s water supply follows national standards (CPHEEO, BIS, and Urban Development Ministry guidelines). The estimated demand is:
- 150 litres per person/day (Low & medium housing)
- 140 litres per person/day (High-density housing & villages)
- 40-45 litres per person/day (Commercial & floating population)
- 45,000 litres per hectare (Industrial use)
- 67,000 litres per hectare (Irrigation – using treated wastewater)
To reduce freshwater demand, treated sewage water will be reused for:
- Irrigation of farms & parks
- Industrial processes
- Green spaces & gardens
Wastewater Management & Recycling
Dholera will have a zero-wastewater discharge policy, meaning all sewage will be treated and reused. The system includes:
- 4 Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs)
- 4 Common Effluent Treatment Plants (CETPs)
- Decentralized treatment for industries & households
How It Works?
- Sewage Collection: Wastewater flows through underground pipes.
- Treatment: Using extended aeration technology (proven & efficient).
- Reuse: Treated water goes to farms, industries, and green spaces.
- Safe Disposal: Remaining water is released into natural streams.
Benefits of Dholera’s Water System
- Sustainable & Eco-Friendly (Reduces freshwater waste)
- Cost-Effective (Uses Narmada Canal, avoiding expensive options)
- Reliable Supply (Modular treatment plants ensure scalability)
- Smart Water Management (Recycling reduces dependency on external sources)
Future Plans
If the Kalpasar Dam is built, it could provide an additional water source. Meanwhile, Dholera’s water treatment and recycling systems ensure long-term sustainability for residents and businesses.
Conclusion
Dholera Smart City is setting a benchmark in sustainable urban planning, with advanced water treatment plants, recycling systems, and smart water management ensuring a green future. Whether it’s the major plants in Ottariya & Hebatpur or supporting infrastructure near Kadipur, DSIR’s water network is designed for efficiency, scalability, and eco-friendly development if you know Latest updates on water treatment and sustainability projects you can view our blog post and know more information
